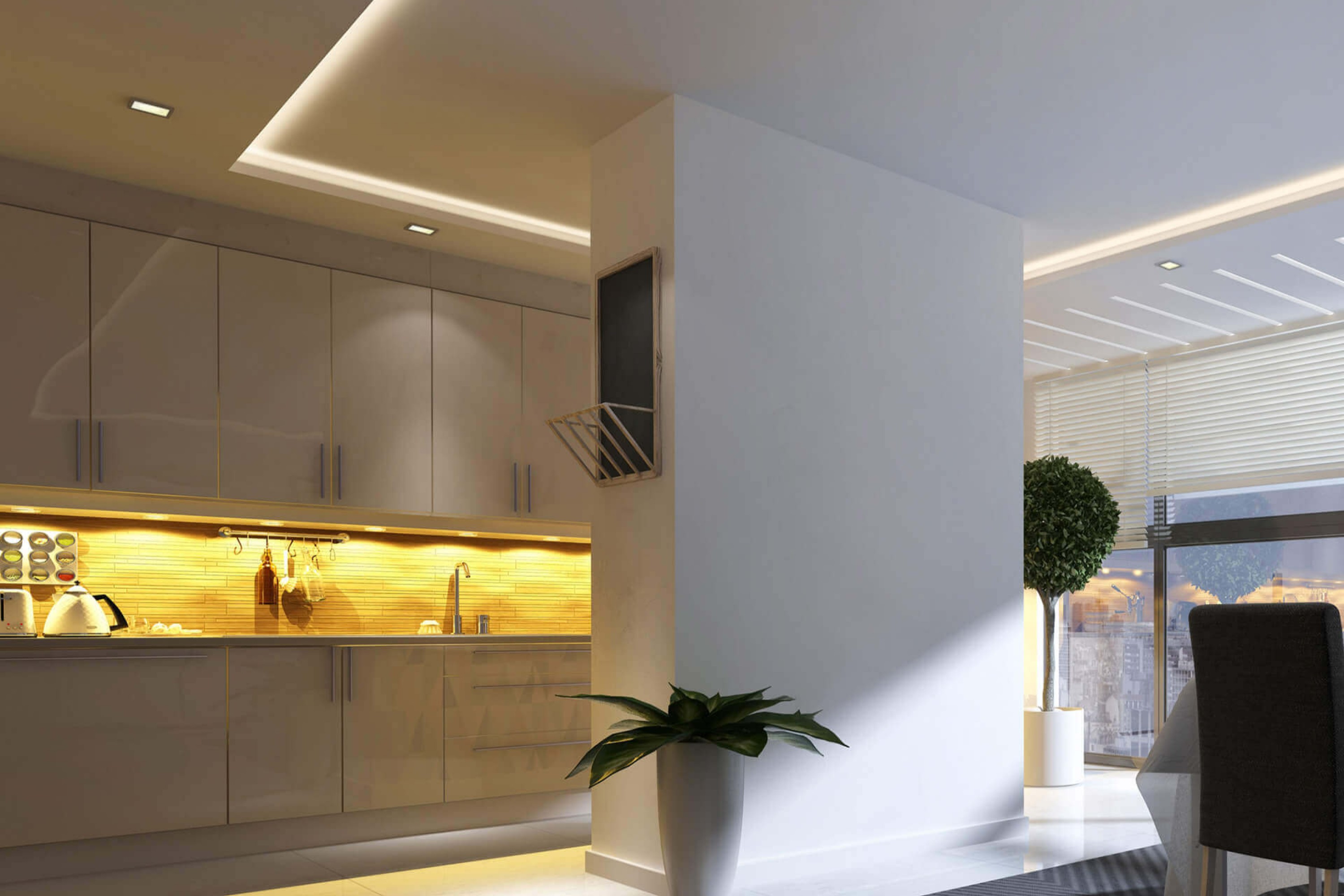
Understanding Dimming Protocols
Dimming isn’t just about ambiance. It can reduce energy consumption and provide more versatile lighting controls for different environments. Dimming protocols govern the communication between the Lighting Controls and light source.
The ideal dimming protocol depends on:
- Type of LED Driver
- Level of control needed (manual vs programmable)
- Environment
- Existing infrastructure
Compatibility is key. Mismatched dimmers and drivers can lead to flickering, buzzing, or no dimming at all.
Here are several dimming systems you may see in the lighting world:
1. 0-10V Dimming
- How it works: Sends a DC voltage signal (between 0V and 10V) to adjust the brightness.
- Benefits: Simple and cost-effective!
2. PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
- How it works: Adjusts LED brightness by rapidly switching between varying intervals.
- Benefits: You can have precise control. It's often used in architectural lighting.
3. Phase-Cut Dimming (TRIAC/ELV)
- How it works: Cuts the AC waveform to lower power to the LED driver.
- Benefits: TRIAC (Leading-edge) is very common in standard dimmers. ELV (Trailing-edge) has a quieter and smoother performance.
4. DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface)
- How it works: DALI is a digital protocol that allows precise, two-way communication between fixtures and controllers.
- Benefits: Highly programmable and ideal for commercial systems.
5. DMX (Digital Multiplex)
- How it works: Originally developed for stage lighting, DMX allows you to control multiple fixtures in real time.
- Benefits: It's power and flexibility make it great for creative lighting designs.
Need help choosing the right controls for your space? At Marvel Lighting, we help our clients find the right solutions for all their lighting needs. Contact us today for assistance.
Join Our Newsletter Now
Be in the light with lighting news and promotions.